
The H3N2 virus is a subtype of the influenza A virus that can cause seasonal flu in humans. Like other flu viruses, H3N2 can cause respiratory illness with symptoms such as fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, body aches, and fatigue.
H3N2 is a highly contagious virus that is easily transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets when infected individuals cough, sneeze or talk. The virus can also survive on surfaces for a short period, allowing it to spread through contact with contaminated objects.

Influenza viruses, including H3N2, undergo frequent mutations, which can result in the emergence of new strains. This is why the flu vaccine is updated every year to provide protection against the most prevalent strains of the virus.
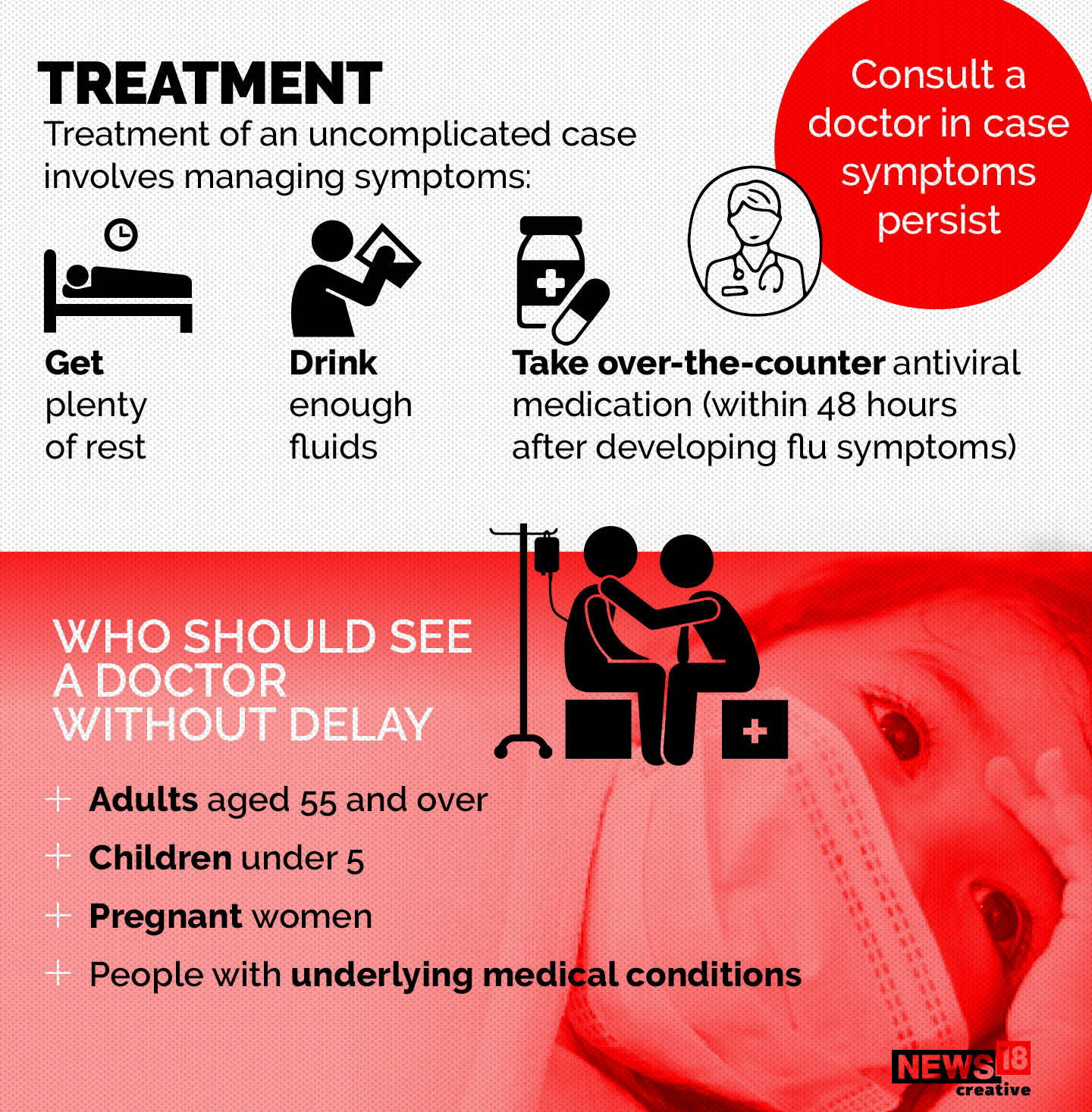
While most people who contract H3N2 will recover without complications, the virus can be particularly dangerous for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Severe cases of H3N2 can lead to pneumonia, hospitalization, and even death.

Preventive measures such as annual flu vaccination, good hand hygiene, and avoiding contact with sick individuals can help reduce the spread of H3N2 and other flu viruses. If you experience flu-like symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to receive appropriate treatment and prevent further transmission of the virus.


0 Comments